Answer The Three Economic Questions
1.3 What Is Economic science?
Learning Objectives
- Define economics and identify factors of production.
- Explicate how economists reply the three key economics questions.
- Compare and contrast economic systems.
To appreciate how a business functions, nosotros need to know something about the economic environs in which it operates. Nosotros brainstorm with a definition of economics and a word of the resources used to produce appurtenances and services.
Resource: Inputs and Outputs
Economic science is the written report of the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Resources are the inputs used to produce outputs. Resources may include any or all of the following:
- Land and other natural resource
- Labor (physical and mental)
- Capital, including buildings and equipment
- Entrepreneurship
Resources are combined to produce goods and services. Land and natural resources provide the needed raw materials. Labor transforms raw materials into goods and services. Capital (equipment, buildings, vehicles, cash, and and so along) are needed for the production procedure. Entrepreneurship provides the skill and creativity needed to bring the other resources together to produce a good or service to be sold to the marketplace.
Considering a business uses resources to produce things, we likewise phone call these resources factors of production. The factors of product used to produce a shirt would include the post-obit:
- The land that the shirt manufactory sits on, the electricity used to run the plant, and the raw cotton from which the shirts are made
- The laborers who make the shirts
- The mill and equipment used in the manufacturing process, likewise as the money needed to operate the factory
- The entrepreneurship skill used to coordinate the other resources to initiate the production procedure and the distribution of the goods or services to the marketplace
Input and Output Markets
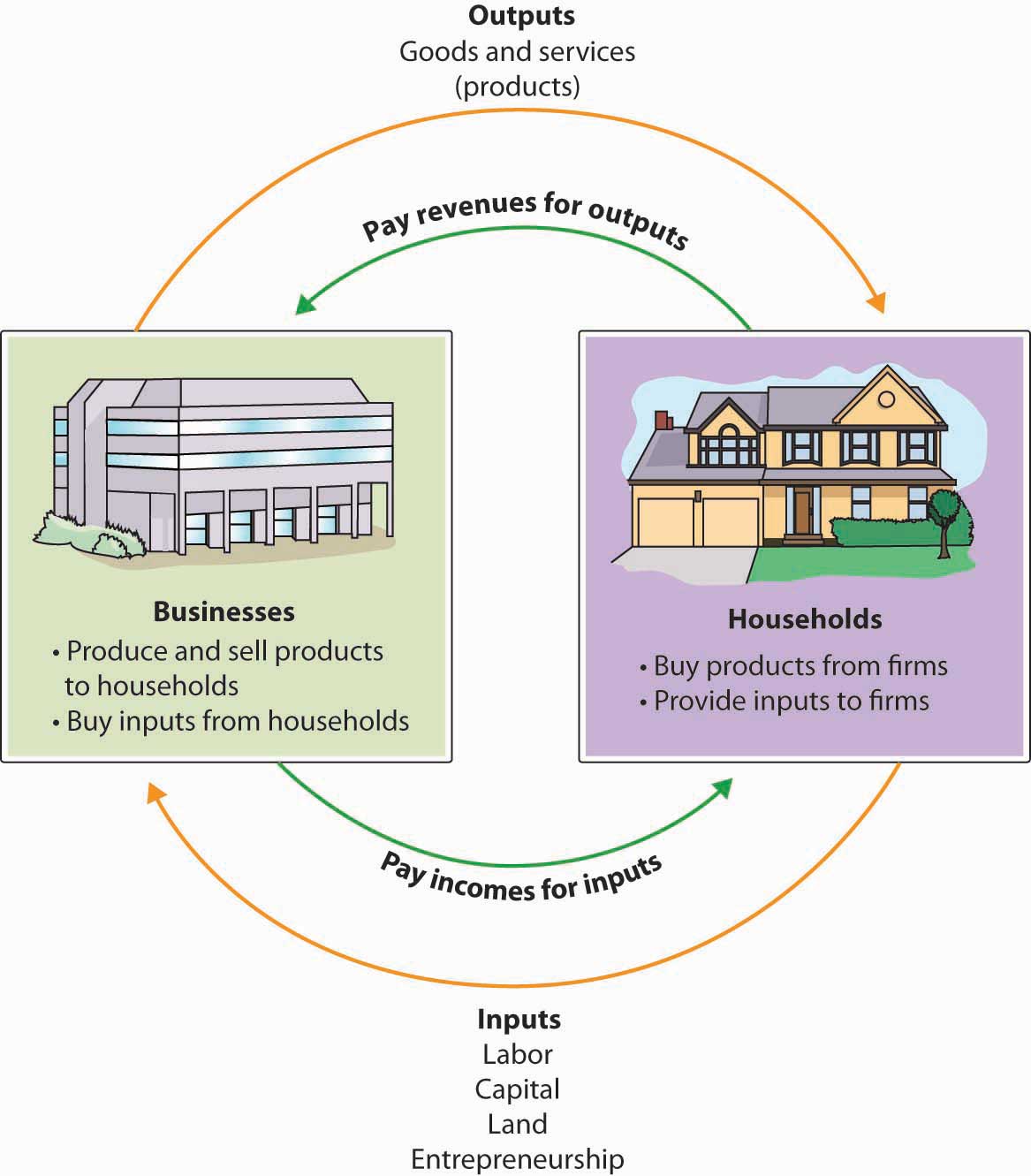
Many of the factors of production (or resource) are provided to businesses by households. For case, households provide businesses with labor (as workers), land and buildings (as landlords), and upper-case letter (every bit investors). In turn, businesses pay households for these resource by providing them with income, such as wages, rent, and involvement. The resources obtained from households are then used by businesses to produce goods and services, which are sold to the same households that provide businesses with revenue. The acquirement obtained by businesses is then used to buy additional resources, and the bike continues. This circular flow is described in Figure 1.3 "The Circular Catamenia of Inputs and Outputs", which illustrates the dual roles of households and businesses:
- Households not merely provide factors of product (or resources) but also consume goods and services.
- Businesses not merely purchase resources but also produce and sell both appurtenances and services.
Figure one.iii The Circular Menstruum of Inputs and Outputs
The Questions Economists Ask
Economists study the interactions betwixt households and businesses and look at the means in which the factors of production are combined to produce the goods and services that people need. Basically, economists endeavor to answer three sets of questions:
- What goods and services should exist produced to come across consumers' needs? In what quantity? When should they exist produced?
- How should goods and services be produced? Who should produce them, and what resources, including technology, should be combined to produce them?
- Who should receive the goods and services produced? How should they be allocated among consumers?
Economical Systems
The answers to these questions depend on a country'south economical arrangement—the means past which a guild (households, businesses, and government) makes decisions virtually allocating resource to produce products and almost distributing those products. The degree to which individuals and business owners, equally opposed to the government, relish liberty in making these decisions varies according to the type of economic organisation. Generally speaking, economic systems can be divided into two systems: planned systems and free market systems.
Planned Systems
In a planned organization, the authorities exerts command over the allotment and distribution of all or some goods and services. The system with the highest level of authorities command is communism. In theory, a communist economic system is one in which the government owns all or virtually enterprises. Central planning by the government dictates which goods or services are produced, how they are produced, and who will receive them. In practice, pure communism is practically nonexistent today, and only a few countries (notably North Korea and Cuba) operate under rigid, centrally planned economic systems.
Nether socialism, industries that provide essential services, such equally utilities, banking, and wellness care, may be government endemic. Other businesses are owned privately. Fundamental planning allocates the appurtenances and services produced past government-run industries and tries to ensure that the resulting wealth is distributed every bit. In contrast, privately owned companies are operated for the purpose of making a profit for their owners. In general, workers in socialist economies work fewer hours, have longer vacations, and receive more than health intendance, instruction, and child-intendance benefits than practise workers in capitalist economies. To offset the loftier cost of public services, taxes are generally steep. Examples of socialist countries include Sweden and France.
Gratis Market System
The economical system in which most businesses are endemic and operated past individuals is the free market system, also known every bit commercialism. Every bit we will see next, in a free market, competition dictates how goods and services will be allocated. Business is conducted with only limited government involvement. The economies of the Usa and other countries, such every bit Japan, are based on capitalism.
How Economic Systems Compare
In comparing economic systems, it'due south helpful to think of a continuum with communism at one stop and pure capitalism at the other, as in Figure 1.4 "The Spectrum of Economical Systems". Every bit you lot move from left to correct, the amount of government command over business diminishes. So, too, does the level of social services, such as wellness care, child-care services, social security, and unemployment benefits.
Figure 1.4 The Spectrum of Economic Systems

Mixed Market Economic system
Though it's possible to take a pure communist system, or a pure capitalist (free market place) system, in reality many economic systems are mixed. A mixed market economy relies on both markets and the authorities to allocate resource. We've already seen that this is what happens in socialist economies in which the government controls selected major industries, such as transportation and health care, while allowing private ownership of other industries. Fifty-fifty previously communist economies, such as those of Eastern Europe and China, are becoming more mixed as they prefer capitalistic characteristics and convert businesses previously endemic by the government to private buying through a process called privatization.
The U.S. Economic System
Like most countries, the United states features a mixed marketplace system: though the U.South. economic system is primarily a free market organisation, the federal regime controls some basic services, such equally the postal service and air traffic control. The U.S. economy besides has some characteristics of a socialist organisation, such every bit providing social security retirement benefits to retired workers.
The free market system was consort by Adam Smith in his volume The Wealth of Nations, published in 1776ane. According to Smith, competition lonely would ensure that consumers received the best products at the best prices. In the kind of competition he assumed, a seller who tries to charge more for his production than other sellers won't exist able to discover any buyers. A chore-seeker who asks more than the going wage won't be hired. Because the "invisible paw" of competition will make the market work effectively, at that place won't exist a need to regulate prices or wages.
Virtually immediately, even so, a tension developed amidst free market place theorists between the principle of laissez-faire—leaving things alone—and government intervention. Today, it's mutual for the U.S. government to arbitrate in the operation of the economic system. For case, regime exerts influence on the food and pharmaceutical industries through the Food and Drug Administration, which protects consumers past preventing unsafe or mislabeled products from reaching the market.
To appreciate how businesses operate, we must start get an idea of how prices are ready in competitive markets. Thus, Section 1.4 "Perfect Competition and Supply and Demand" begins by describing how markets constitute prices in an environment of perfect competition.
Fundamental Takeaways
- Economics is the study of the product, distribution, and consumption of appurtenances and services.
- Economists address these three questions: (1) What goods and services should be produced to meet consumer needs? (2) How should they be produced, and who should produce them? (3) Who should receive goods and services?
- The answers to these questions depend on a land'due south economic system. The primary economic systems that exist today are planned and gratuitous marketplace systems.
- In a planned system, such every bit communism and socialism, the authorities exerts control over the production and distribution of all or some goods and services.
- In a free market organisation, too known as capitalism, business is conducted with just limited authorities involvement. Competition determines what appurtenances and services are produced, how they are produced, and for whom.
Exercises
- If y'all started a business organisation that made surfboards, what factors of product would you lot demand to brand your product? Where would you get them? Where would you notice the money you'd need to pay for boosted resources?
- Which three central questions exercise economists effort to answer? Will answers to these questions differ, depending on whether they're working in the Us or in Cuba? Explain your answer.
iCo-ordinate to many scholars, The Wealth of Nations not just is the most influential volume on costless-market capitalism but remains relevant today.
Answer The Three Economic Questions,
Source: https://open.lib.umn.edu/exploringbusiness/chapter/1-3-what-is-economics-2/#:~:text=Key%20Takeaways-,Economics%20is%20the%20study%20of%20the%20production%2C%20distribution%2C%20and%20consumption,should%20receive%20goods%20and%20services%3F
Posted by: fowlerproder.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Answer The Three Economic Questions"
Post a Comment